Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
Caris’ whole transcriptome sequencing (WTS) uses the capabilities of high-throughput sequencing to gain insight into the RNA profiles of patient tumors. WTS provides extremely broad coverage and strong resolution (depth) into the dynamic nature of the transcriptome.
WTS enables gene fusion detection and RNA splice variant detection all from one streamlined test. The test identifies fusions independent of the breakpoints in DNA and has the ability to detect rare, or novel, fusion events better than targeted RNA sequencing or DNA-based methods. By providing broad exon coverage and capturing essentially all possible fusion partners, whole transcriptome sequencing can reliably detect different types of gene fusions, while reducing false positives caused by non-expressed rearrangements.
| Features | MI Transcriptome™ |
|---|---|
| Genes covered | Essentially All (~23k) genes; Clinically actionable genes will be highlighted on Caris Reports and unclassified RNA alterations will be available separately |
| Reads/Sample | 17 million reads |
| Assay method | Hybrid capture |
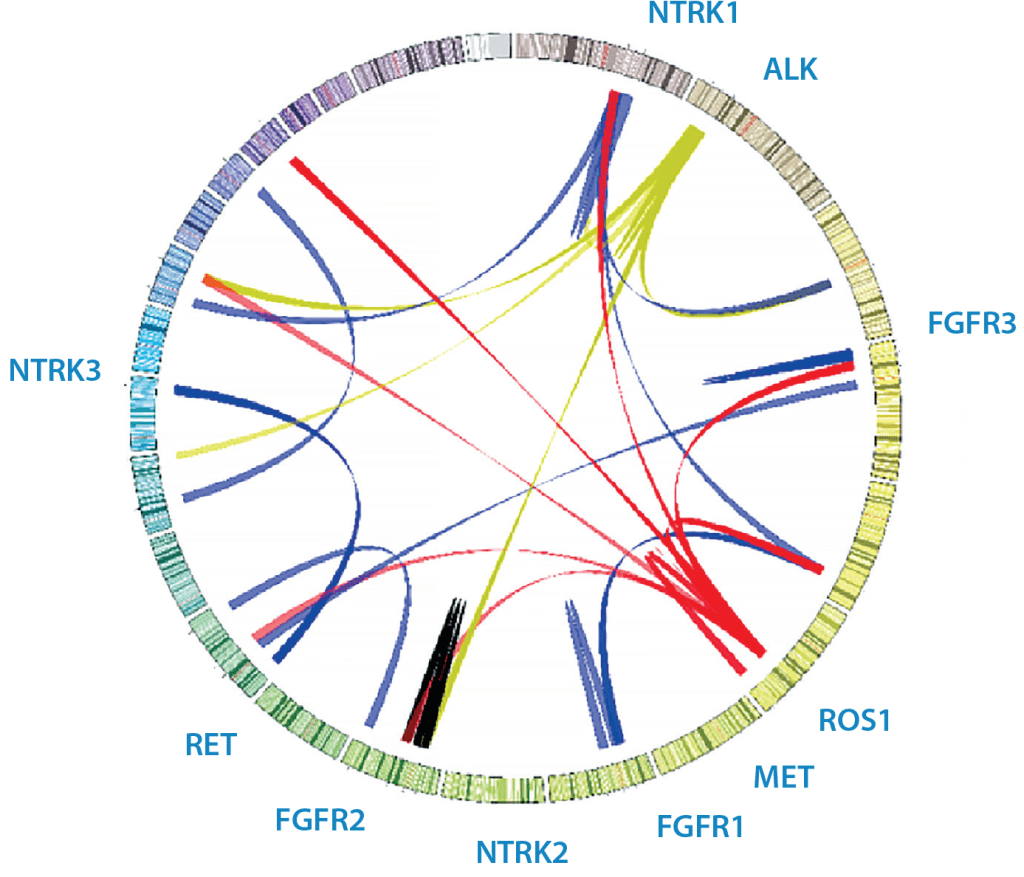
Figure 1: Sample Circos plot of various clinical fusions
With Whole Exome Sequencing (WES), Whole Transcriptome Sequencing (WTS), extensive proteomic testing services, and advanced machine-learning capabilities, Caris molecular profiling is the most comprehensive and clinically relevant molecular profile for cancer patients in the industry.
Advantages of RNA Analysis via Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
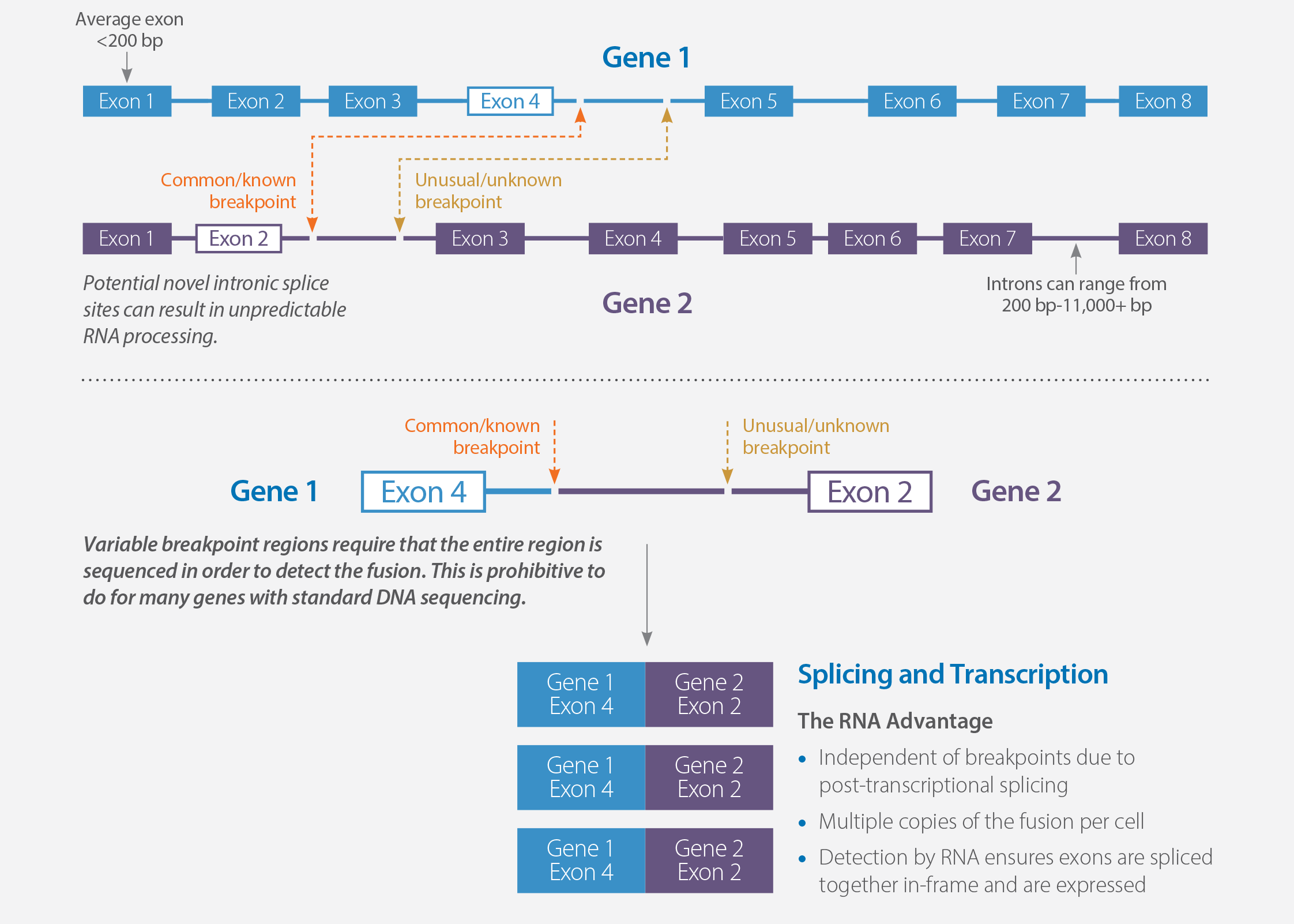
- DNA sequencing can detect some chromosomal rearrangements in formalin-fixed samples; however, locating breakpoints within large regions of repetitive intronic sequence is difficult using short sequence reads
- DNA sequencing CANNOT determine if a fusion gene is expressed in mRNA
- DNA sequencing CANNOT detect read-through fusions
Variant Transcripts
- DNA sequencing cannot DIRECTLY detect variant mRNA transcripts that result from alternate mRNA splicing
- MI Transcriptome RNA sequencing WILL pick up variant transcripts by looking at the spliced mRNA directly
- RNA sequencing provides more relevant information when analyzing biological functions; MI Transcriptome will provide an estimate of gene expression levels to feed pathway analysis tools
| Fusion Analysis Method | # of Genes | Clinical Actionability | Fusion Expression |
|---|---|---|---|
| MI Transcriptome | Essentially all genes | Can detect gene fusions | Can identify if fusion is expressed |
| DNA Sequencing | Limited (hot spots) | Can detect rearrangements that may not always result in gene fusions | Cannot identify if fusion is expressed |
Figure 2: Diagram showing advantages of MI Transcriptome over DNA Sequencing for fusion analysis
Example: An ALK fusion may be found at the DNA level but it may not be expressed as RNA. Some fusion partners such as EML4 result in dramatic overexpression of ALK and increase in its kinase signaling. However, other fusion partners may not result in ALK overexpression and thus would not potentiate the oncogenic ALK kinase activity. Such cases are unlikely to derive significant benefit from targeted ALK therapy.
RNA-based analysis, via Whole Transcriptome Sequencing, is the best method to detect clinically relevant aberrations, because the presence of RNA transcripts ensures that the alterations have been transcribed from DNA to RNA. MI Transcriptome also has the potential to discover previously uncharacterized events, which is important when identifying patients who may derive a strong response to targeted therapy. The test uses the same tissue requirements as Caris’ DNA tumor profiling and delivers results in the same turnaround time.
Please complete the form below to have a Caris Scientific Rep (Molecular Science Liaison) contact you directly.
"*" indicates required fields
Complete Gene Coverage with Caris Molecular Testing
As the pioneer in precision medicine, Caris was the first to provide comprehensive Whole Exome and Whole Transcriptome sequencing for every patient. Each Caris molecular profiling order includes next-generation sequencing of all 23,000 genes.
Looking for a specific gene? Use the full gene search below to verify that it is included in Caris profiling, or browse the list of genes most commonly associated with cancer.
| Whole Transcriptome Sequencing – Genes most commonly associated with cancer listed below. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fusions (RNA) | Variant Transcripts (RNA) | ||||||||
| ABL | BRD3 | FGFR3 | INSR | MYB | NUMBL | PRKCA | RSP03 | AR-V7 | |
| AKT3 | BRD4 | ERG | MAML2 | NOTCH1 | NUTM1 | PRKCB | TERT | ||
| ALK | EGFR | ESR1 | MAST1 | NOTCH2 | PDGFRA | RAF1 | TFE3 | EGFR vIII | |
| ARHGAP26 | EWSR1 | ETV1 | MAST2 | NRG1 | PDGFRB | RELA | TFEB | ||
| AXL | FGR | ETV4 | MET | NTRK1 | PIK3CA | RET | THADA | MET Exon 14 Skipping | |
| BCR | FGFR1 | ETV5 | MSMB | NTRK2 | PKN1 | ROS1 | TMPRSS2 | ||
| BRAF | FGFR2 | ETV6 | MUSK | NTRK3 | PPARG | RSPO2 | |||
*Not available in all locations.
Caris Molecular Profiling Menu by Region
United States
Review and download the Caris molecular profiling testing menu for United States cases.
New York
Review and download the Caris molecular profiling testing menu for New York state cases.
International*
Review and download the Caris molecular profiling testing menu for International cases.
*Excluding EEA, EU, CH countries.
Caris Molecular Profiling Menu by Region
International & US
New York
European Union (EU)
RNA is the Superior Method of Gene Fusion Analysis
DNA vs RNA – Direct Comparison Shows RNA is the Superior Method for Fusion Analysis
A recent study by Benayed, et al.1 shows that RNA fusion analysis2 identifies additional alterations as compared to DNA fusion analysis3.- 2,522 NSCLC cases were sequenced using standard DNA-based methods. Of those, 232 cases lacked an oncogenic driver.
- These 232 driver-negative cases were then RNA sequenced and 36 (15.5%) were found to have oncogenic drivers that were not detected by DNA sequencing, 33 of which were clinically actionable.
- Importantly, in this analysis DNA sequencing did not detect any fusions in NTRK 2/3 that RNA was able to detect.
- The data from Benayed, et al. are significant, but still limited by the use of targeted RNA sequencing. Further investigation using WTS would likely identify even more fusion partners.
NSCLC NCCN guidelines suggest using RNAseq to maximize the number of fusions detected5
| Fusion/Variant | # detected by RNA seq not detected by DNA seq |
|---|---|
| ALK | 4 |
| BRAF | 1 |
| FGFR2 | 1 |
| MET (exon14) | 6 |
| NRG1 | 5 |
| NTRK2 | 1 |
| NTRK3 | 2 |
| RET | 3 |
| ROS1 | 10 |
N = 232
RNA-Based Fusion Analysis of NTRK1/2/3 Finds 50% More Clinically Actionable NTRK3 Fusion Partners than DNA
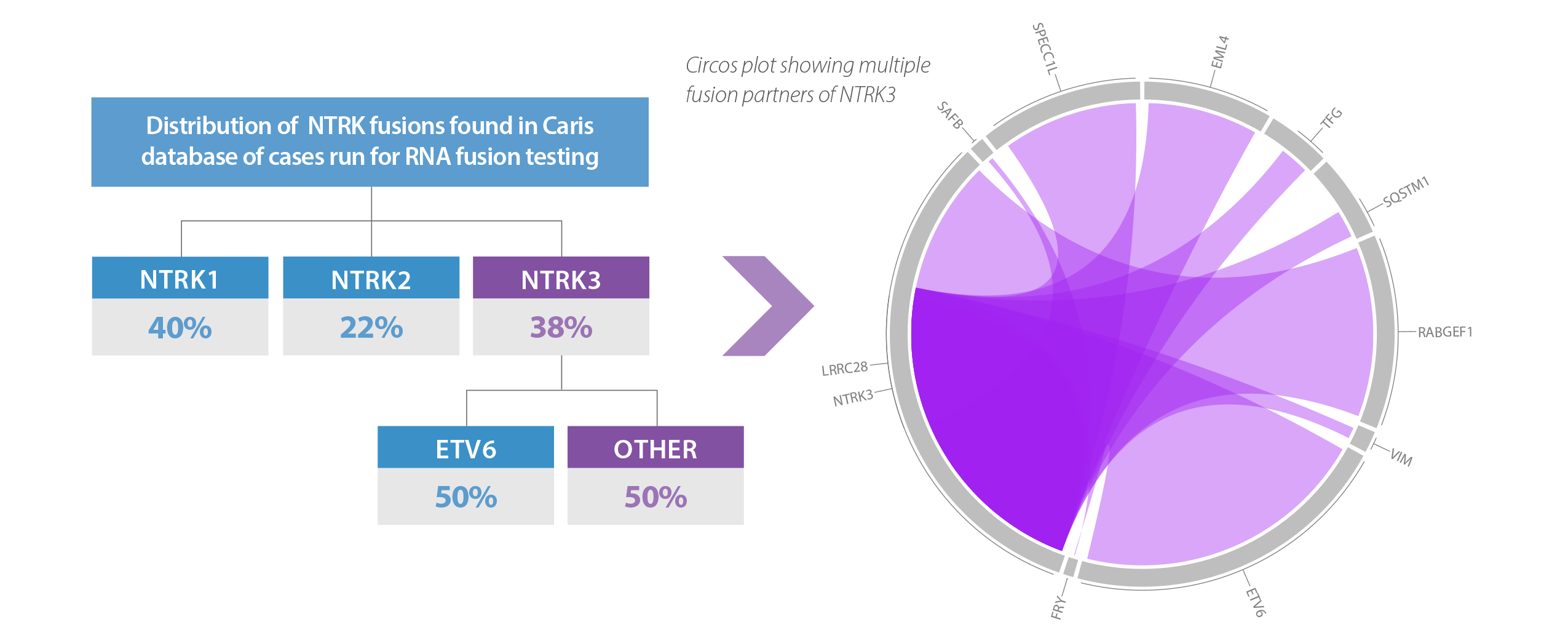
Whole Transcriptome Sequencing Captures All Potential Fusion Partners
WTS Overcomes Limitations of DNA Based Fusion Analysis
Order Profiling
Place an order today for a comprehensive, personalized Caris profiling report.